Luteolin Background and Benefits
Luteolin is a chemical that is classified as a citrus bioflavonoid. It is a yellow crystal in pure form, which is typical for flavonoids. Luteolin has many uses as a health supplement due to its antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties. These properties allow luteolin to scavenge reactive compounds containing oxygen and nitrogen, which can cause cellular damage. Additional biological effects of luteolin include the activation of the dopamine transporter.
Luteolin is produced by many plants, many of which are edible. Significant dietary sources of luteolin include citrus fruits, especially oranges. Broccoli, carrots, celery and green pepper are vegetables that also contain luteolin. Herbs with luteolin include parsley, peppermint, rosemary and oregano. Peanut hulls are one of the most important commercial sources of luteolin. These hulls are an inexpensive source since they’re a by-product of processed peanuts.
Ethanol reflux is a common method of extracting luteolin from peanut hulls. This process essentially consists of mixing the powdered hulls with 70 percent ethanol to obtain a liquid/solid ratio of 20:1. This mixture is then heated at 85 degrees Celsius for at least 1.5 hours. The vapor that comes off the mixture is high in luteolin, which can be further concentrated to a high level of purity.
1) Luteolin Fights Cancer
Luteolin interferes with nearly all types of cancer cells.
It inhibits the growth of new blood vessels in tumors, the metabolism of carcinogens, as well as stopping the progression of the cell cycle in cancer cells. Luteolin also induces cell death in cancer cells.
In mice, luteolin suppressed growth of tumors formed from human skin carcinoma, hepatoma, and human ovarian cancer cells.
Luteolin inhibited the incidence rate of tumors and decreased the size of tumors significantly.
Long term treatment did not show any apparent toxicity in rats at a dose of 30mg/kg, implying that luteolin is relatively safe as an anticancer agent.
Through in vitro and vivo experiments, luteolin was found to have therapeutic and preventative activities against cancer associated with estrogen.
2) Luteolin Decreases Inflammation
Experiments with animals show that luteolin suppresses bacteria-induced inflammation.
Luteolin is also found to suppress two major pathways involved in response to inflammation, which greatly reduces both acute and chronic inflammation.
Luteolin suppressed pro-inflammatory marker expression and cytokine expression in LPS-activated microglia.
In an experiment on rats with toxin-induced uveitis, luteolin had great success in anti-inflammatory treatment, comparable to that of prednisolone.
Luteolin can also inhibit colitis (inflammation in the colon).
3) Luteolin is an Antioxidant
Luteolin is an oxygen scavenger. It was found to inhibit reactive oxygen species, which induce damage of lipids, DNA, and protein.
4) Luteolin is a Natural Sun Protectant
Luteolin potently inhibited UVB-induced MMP-1 expression and wrinkle formation in vitro and in vivo and therefore may be used for prevention of UVB-induced skin aging.
5) Luteolin Improves Heart Function
In an experiment on rats, luteolin was found to inhibit cell death in the cells of the heart. This suggest that luteolin can be used in the prevention and treatment of cardiovascular diseases.
Luteolin substantially increased cell life while reducing evidence of oxidative stress-induced damage in the cells.
Luteolin also improved the recovery of heart cells contracting function following simulated injury caused by loss of blood flow, by reducing oxidative stress.
Luteolin significantly induces genes related to antioxidant defense.
6) Luteolin Protects the Brain From Neurological Impairments
Luteolin treatment in rats reduced brain damage caused by kainic acid by reducing glutamate levels, mitigating inflammation, and enhancing the hippocampus.
Tests on flies expressing a neurological impairment that resembles amyloidosis showed that luteolin rescued the impairment.
Luteolin induces neurite outgrowth through CREB activation. CREB activation is the mechanism underlying its effects on memory enhancement.
Luteolin can go through the blood-brain-barrier (BBB), which shows anti-amnesic effects against the toxicity of amyloid in mice.
In an experiment on rats with streptozotocin induced Alzheimer’s disease, luteolin significantly improved spatial learning and memory impairment.
Luteolin also protects against high-fat diet-induced cognitive defects in obesity mice.
7) Luteolin is an Antiviral
Luteolin was found to have potent antiviral activity against Japanese encephalitis virus (JEV).
Luteolin reduced the number of Epstein-Barr virus reactivating cells and reduced the production of the virus. It does this by repressing the activities of the promoters of the immediate-early genes Zta and Rta.
In mice with hepatitis B virus (HBV), Luteolin reduced HBV DNA replication, suggesting that it may be used for anti-HBV therapy.
8) Luteolin Prevents Cataracts
In rats, luteolin enhanced the antioxidant potential and lowered the oxidative damage to the lens’ of rats in selenite-induced cataracts. It also improved the membrane integrity of the lens.
9) Luteolin May Be Therapeutic for Multiple Sclerosis
Multiple Sclerosis is a disease that affects the immune system – nerve damage causes pain and fatigue. Luteolin has anti-oxidant and anti-inflammatory effects which can reduce the effects of multiple sclerosis.
10) Luteolin Inhibits Mast Cells
Luteolin inhibits mast cells and mast cell-dependent T cell activation, factors which contribute to multiple sclerosis.
11) Luteolin Has Anti-Depressant Effects
The endoplasmic reticulum in a cell can undergo stress, which can cause cell death. In the brain, neuronal cells undergo cell death and this can cause symptoms of depression.
Luteolin significantly suppresses cell death by relieving endoplasmic reticulum stress.
Uses of Luteolin
The uses of luteolin in health supplements primarily relates to its ability to manage inflammatory conditions. These uses include support for memory and the nervous system in addition to antioxidant effects.
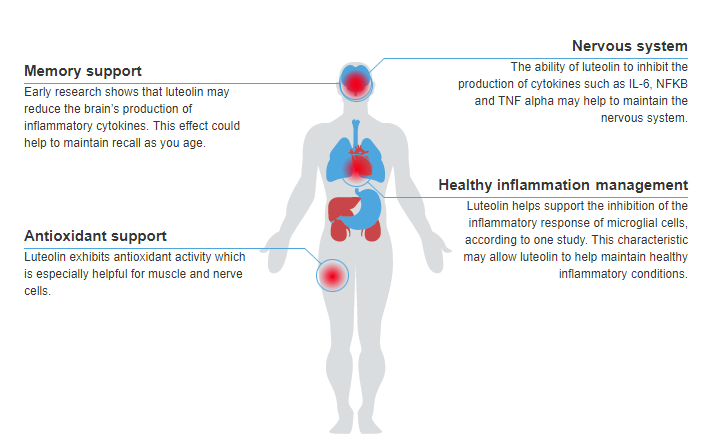
Signs You May Need Luteolin
Poor neurological functions are generally the most significant indications that you may need luteolin, especially if you are over the age of 50. These functions include memory, learning and motor skills. Signs of oxidative stress such as skin lesions and wrinkles are some of the more visible signs that you may need luteolin. Inflammatory conditions that affect the nervous system are some of the chronic signs that luteolin may benefit you. Auto-immune disorders may also mean that you require additional luteolin.






Leave A Comment